The Male Penis
The Male Penis
The penis is the male sex organ. Its primary functions include reproduction and urination. No two penises are the same, and they can vary in length, girth, and appearance. Penises mostly all include the same anatomy, which allows them to perform their functions.
Knowing the anatomy and function of the penis is important for good health. Noticing any changes in the appearance, sensation, or performance of the penis can indicate an underlying issue that may require medical attention.
What is the penis?
The penisTrusted Source is the male copulatory organ. The term penis typically refers to the root, body, and glans of the genitals. The rest of the male sexual anatomy includes other external parts such as the scrotum, and internal parts such as the testicles.
The penis contains soft, spongy tissue as well as muscles, fibrous tissue, veins, arteries, and the urethra. These allow the penis to perform its functions.
Functions
The two mainTrusted Source functions of the penis include sexual intercourse and micturition (urination).
When a person experiences arousal, the penis fills with blood, causing an erection. As such, erectile function is closely related to cardiovascular health.
The rigidity of the erection enables a person to penetrate a partner and have sex. Following sexual activity or manual stimulation, a person can then ejaculate. After ejaculation or loss of arousal, the penis can return to a flaccid state. The penis also plays an important urinary role. The penis contains the urethra, which allows passage of urine from the bladder to the urethral opening, enabling a person to expel urine from the body.
Anatomy of the penis
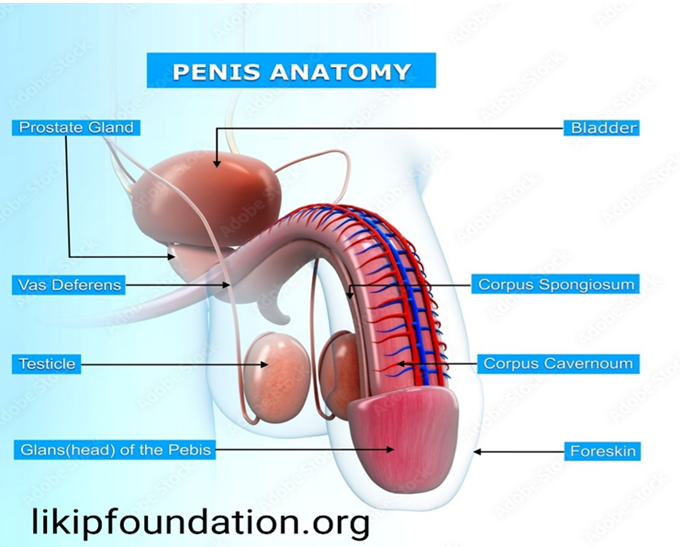
The penis has three parts.
- Root: This is the part of the penis attached to the body and is not visible externally. It contains three erectile tissues, which include two crura and the bulb of the penis, and two muscles called the ischiocavernosus and bulbospongiosus. The urethra connects to the bladder and passes through all parts of the penis.
- Body: The body, or shaft, is the free part of the penis between the root and glans. It contains three cylinders of erectile tissue, which include two corpora cavernosa and the corpus spongiosum.
- Glans: This is the most distal, or end, part of the penis. It gets its shape from the bulbous expansion of the corpus spongiosum. The glans also features the urethral opening, which is where the urethra ends, allowing a person to expel urine and semen.
The erectile tissues
These are the tissues that fill with blood during arousal, which allow a person to have an erection. In the root, this starts with the left and right crura and the bulb of the penis, which is in the midline of the penile root.
The left and right crura continue into the body of the penis and form the two corpora cavernosa. The bulb continues into the body and forms the corpus spongiosum. The urethra runs through the corpus spongiosum, which prevents it closing during an erection. The corpus spongiosum then expands to form the glans of the penis.
Muscles
The bulbospongiosusTrusted Source muscle is associated with the bulb of the penis. It contracts to help empty the urethra of any residual semen and urine. The ischiocavernosusTrusted Source muscle surrounds the left and right crura. It contracts to force blood in the crura into the corpora cavernosaTrusted Source, which helps a person to maintain an erection.
Fascial coverings
Each erectile tissue has fascial coverings, or bands of connective tissue, which surround and support them. This includes the deep fascia of the penis, or Buck’s fascia, and the tunica albuginea. These coverings help protect the penis and help maintain an erection by preventing blood from leaving the erectile tissues.
Ligaments
The suspensory and fundiform ligaments support the root of the penis and attach to the surrounding structures. The suspensory ligament holds the penis close to the pubic bone and supports it when erect. The fundiform ligament also supports the penis, surrounding it like a sling.
Skin
Skin covers the entire body of the penis. People may also have a retractable layer of skin that covers the glans. People may refer to this as the prepuce, or foreskin. The foreskin connects to the surface of the glans by a fold of skin known as the frenulum.
Types of penises
Just like any other body part, the penis can vary greatly from person to person. For penises, people typically notice differences in measurements and appearance.
Penises come in different lengths and girths, and this changes when flaccid or erect. Some people may measure the base-to-head ratio. There is no single size that is better than others, and people will have their own personal preference. There are more important factors for sexual compatibility than just penis size.
When erect, some penises may be straight, while others may have a bend. Penile curvature is common, rarely painful, and does not usually make penetrative sex more difficult. In fact, in some cases, penile curvature may be more pleasurable for the receiving partner.
Some people may or may not have a foreskin on their penis. Some individuals may have the foreskin surgically removed in a procedure called circumcision.
Diseases of the penis
There are many conditions that can affect the penis. These may include:
- Penis infections: Many infections can affect the penis and cause painful symptoms such as redness, swelling, and itching. These can include balanitis, posthitis, balanoposthitis, and phthiriasis.
- Sexually transmitted infections (STIs): These refer to infections that people typically acquire through sexual contact. These can include chlamydia, gonorrhea, genital warts, and syphilis.
- Erectile dysfunction: This typically refers to when a person has difficulty getting or keeping a firm enough erection to have sex.
- Priapism: This is when blood becomes trapped in the penis and can cause a prolonged and painful erection that can result in permanent tissue damage.
- Chordee: This is a condition where bands of tissue pull on the penis, giving it a bent appearance.
- Peyronie’s disease: This condition occurs when scar tissue forms under the penis’ skin and causes an abnormal curvature of the penis.
- Urethritis: Inflammation and swelling of the urethra can result in difficulty or pain when urinating.
- Micropenis: This refers to an abnormally small penis, typically due to hormonal or genetic issues.
- Buried penis: This is a medical condition where excess skin and fat cover the penis, making it less visible.
- Penile cancer: This is a rare type of cancer that develops on or in the penis.
How to have a Healthy Penis
It is advisable for a person to regularly wash their penis using a mild soap. People should avoid abrasive or heavily scented products as they can irritate the penis. People can also use this time to check their penis for anything that appears unusual or different. This can include checking the testicles for any lumps.
People should also consider using barrier methods, such as condoms, when having sexual intercourse, and undergo regular sexual health screenings, even if they are in a monogamous relationship.Other tips can include general advice to improve overall health. This may involve eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, limiting alcohol consumption, and trying to avoid smoking
What is ‘normal’ or average penis size?
Many people experience anxiety about whether their penis is big enough and if it will satisfy a sexual partner. This can affect a person’s self-confidence and self-image. Often, however, these fears are unfounded. In 1996, experts carried out a study that led to a set of guidelines for when a person may need surgery for penis enlargement. The study measured the penile dimensions of 80 males before and after drug-induced erections. The researchers concluded that the average penis size was 8.8 cm (3.5 in) e when flaccid and 12.9 cm (5.1 in) when erect.The study also found that the size of a person’s erect penis did not correlate with their flaccid penis size. In other words, a penis may have different lengths when flaccid but similar lengths when erect. They also found no link between age and penis size. The researchers concluded: “Only men with a flaccid length of less than 4 cm (1.6 in), or a stretched or erect length of less than 7.5 cm (3 in) should be considered candidates for penile lengthening.”
Micropenis and buried penis
Some people are born with micropenis, when a penis is unusually small, usually due to hormonal or genetic factors. A micropenis fulfills the same functions as an average-sized penis, but people may feel dissatisfied with its appearance. Hormonal treatment or surgery can increase its size if a person wishes. Sometimes, an average-sized penis may appear small due because there is additional skin around it. People may refer to this as a buried penis, and surgery can resolve it.
How to measure a penis
To measure penis length, press a ruler into the groin and measure from the base of the penis to the tip. To measure penis girth, wrap a measuring tape around the widest part of the penis.
What size penis do women want?
Does longer penis increases sexual satisfaction?
Another concern for some males is that a longer penis increases sexual pleasure for one or both partners. However, at least one study from 2001 suggests that people tend to rate girth as more important than length for satisfaction.
It is also important to note that several other factorsTrusted Source play a role in sexual satisfaction, including individual-, partner-, and relationship-related factors. For example, research indicates that communication, mood, and desire all play a role.

Also, some experts suggest that being romantic and sensitive is more important than penis size for sexual satisfaction among females.
factors that affect penis size
The following factors affect penis size:
Hormones
Just.as estrogen and progesterone affect female sexual characteristics, such as breasts, hips, and fat storage, male sex hormones, or androgens, contribute to testicular and penile growth.
During puberty, the pituitary gland produces more luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). LH promotes testosterone production in the Leydig cells of the testicles, and FSH promotes sperm production.
Variations in testosterone levels during pregnancy may cause penile abnormalities. For example, the mother may not produce enough human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) hormone. The hCG hormone stimulates testosterone development in the fetus.
Rare conditions, such as 5 alpha reductase deficiency and congenital adrenal hyperplasia, also affect testosterone levels and may affect genital appearance.
Even if testosterone levels are normal, some medical conditions may stop a person’s body from responding to testosterone correctly. This response is called androgen insensitivity.
When any of these hormonal issues arise, the penis of a male fetus may not develop in the usual way.
Environment
Environmental pollutants, such as pesticides, plasticizers, and other chemicals, may have a negative effect on penis size. These chemicals may act as endocrine disruptors and impact gene and hormone expression.
Epigenetics is a growing area of science investigating how the environment may affect gene expression.
Researchers believe epigenetics plays a role in development and disease. They suspect it may influence hormone function and have a role in hormone disorders.
Studies in 2015 and 2016 both suggest that prenatal exposure to chemicals, such as phthalates, negatively impacts the genital development of male newborns.
A 2019 study also suggests that epigenetic-associated dietary influences may slow genital progression in adolescent boys.
Nutrition
Malnutrition in the womb and throughout life may impact hormones and affect growth and development.
Furthermore, malnutrition in adolescence, as is seen in anorexia or bulimia, can delay normal puberty.
While individuals undergoing delayed puberty typically catch up eventually, symptoms of delayed puberty include a smaller penis and testicles.
Other factors
Genetics are the strongest predictors of penis size. However, factors, such as body fat and the presence or absence of pubic hair, can make the penis appear larger or smaller without affecting its true size.
When exposed to cold temperatures, the blood vessels in the penis constrict. This physiological reaction causes the penis to shrink temporarily.
Risks of trying to increase size
The penis enlargement or male enhancement industry claims that enlargement procedures, vacuum devices, pills, and creams increase penis size.
However, there is limited research for many of these methods, and they may come with serious risks.
The majority of people seeking penis enlargement have average-sized penises, meaning that they are of adequate size for sexual activity and urination.
The Urology Care Foundation only recommends penis enhancement surgery for people with a rare condition called micropenis where a penis is two or more standard deviations below the average size.
The American Urological Association states that there is not enough high-quality evidence to support the safety or efficacy of penile augmentation surgery.
Potential risks of trying to increase penis size include:
- swelling, infection, or scarring after surgery
- damage due to overusing a vacuum pump or stretching devices
- contact dermatitis that topical products may trigger
- allergic reactions to ingredients in pills
- erectile dysfunction
HOW DO DOCTORS TREAT SMALL PENIS?
Hormone treatment, surgery, and other techniques can increase the size of a very small penis. However, these treatments carry risks , and most people do not have a small enough penis to warrant these options. Doctors do not usually recommend treatment unless a penis has a flaccid length of under 4 cm (1.6 in) or a stretched or erect length of less than 7.5 cm (3 in).Many males worry about the appearance of their penis at some point in their lives. Common myths often fuel these concerns. Knowing the facts about average penis size can help people become more confident about their body.
As research seems to suggest, most males overestimate the average penis size. Studies also indicate that most females are happy with the size of partner’s penis. Those who have persistent concerns about their penis size may benefit from seeing a doctor or mental health professional for support and guidance.
Sexual weakness

What is sexual dysfunction in males?
Sexual dysfunction is any physical or psychological problem that prevents you or your partner from getting sexual satisfaction. Male sexual dysfunction is a common health problem affecting men of all ages, but is more common with increasing age. Treatment can often help men suffering from sexual dysfunction.
The main types of male sexual dysfunction are:
- Erectile dysfunction (difficulty getting/keeping an erection).
- Premature ejaculation (reachingorgasm too quickly).
- Delayed or inhibited ejaculation (reaching orgasm too slowly or not at all).
- Low libido (reduced interest in sex).
What causes sexual dysfunction in males?
Physical causes of overall sexual dysfunction may be:
- Low testosterone levels.
- Prescription drugs (antidepressants, high blood pressure medicine).
- Blood vessel disorders such as atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and high blood pressure.
- Stroke or nerve damage from diabetes or surgery.
- Alcoholism and drug abuse.
Psychological causes might include:
- Concern about sexual performance.
- Marital or relationship problems.
- Depression, feelings of guilt.
- Effects of past sexual trauma.
- Work-related stress and anxiety.
How does sexual dysfunction affect men?
The most common problems men face with sexual dysfunction are troubles with ejaculation, getting and keeping an erection, and reduced sexual desire.
Ejaculation disorders
Problems with ejaculation are:
- Premature ejaculation (PE): Ejaculation that occurs before or too soon after penetration.
- Inhibited or delayed ejaculation: Ejaculation does not happen or takes a very long time.
- Retrograde ejaculation: At orgasm, the ejaculate is forced back into the bladder rather than through the end of the penis.
While in many cases PE is due to performance anxiety during sex, other factors may be:
- Temporary depression.
- History of sexual repression.
- Low self-confidence.
- Lack of communication or unresolved conflict with partner.
Studies suggest that the breakdown of serotonin (a natural chemical that affects mood) may play a role in PE. Certain drugs, including some antidepressants, may affect ejaculation, as can nerve damage to the back or spinal cord.
Physical causes for inhibited or delayed ejaculation may include chronic (long-term) health problems, medication side effects, alcohol abuse, or surgeries. The problem can also be caused by psychological factors such as depression, anxiety, stress or relationship problems.
Retrograde ejaculation is most common in males with diabetes who suffer from diabetic nerve damage. Problems with the nerves in the bladder and the bladder neck force the ejaculate to flow backward. In
other men, retrograde ejaculation may be a side effect of some medications, or happen after an operation on the bladder neck or prostate.
Erectile dysfunction (ED)
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is the inability to get and keep an erection for sexual intercourse. ED is quite common, with studies showing that about one half of American men over age 40 are affected.
What causes erectile dysfunction?
There are numerous potential causes of erectile dysfunction.
Neurologic causes include:
- Stroke
- Spinal cord or back injury
- Multiple sclerosis
- Dementia
- Pelvic trauma
- Prostate surgery (even with nerve-sparing surgeries it can take up to 24 months to regain normal sexual function)
- Priapism
- Nervous system tumor
- Epilepsy
- Diabetic neuropathy
Vascular causes include:
- Arteriovenous fistula
- Diabetes
- Atherosclerosis
- Congenital anomaly
Hormonal causes include:
- Low testosterone blood level (The patient can achieve an erection but it won’t always be turgid enough for vaginal penetration.)
- Hyperprolactinemia
- Hyperthyroidism
- Hypothyroidism
- Cushing’s disease
- Addison’s disease
Pharmacological causes include:
- Antidepressants (mainly SSRIs)
- Spironolactone
- Sympathetic blockers (clonidine, guanethidine, or methyldopa)
- Thiazide diuretics
- Ketoconazole
- Cimetidine
Penile dysfunction causes include:
- Peyronie’s disease
Psychiatric causes include:
- Loss of feeling toward the other person
- Stress
- Fear of non-performance
Functional causes include:
- Bicycling irritating the nerves and tissue of the penis
What are the risk factors for erectile dysfunction?
The risk factors for erectile dysfunction include:
- Obesity
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Cardiovascular disease
- Medication use
- Obstructive sleep apnea
- Restless leg syndrome
- Systemic sclerosis (scleroderma)
- Peyronie’s disease
- Prostate cancer treatment
- Diseases affecting blood flow such as hardening of the arteries.
- Nerve disorders.
- Stress, relationship conflicts, depression and performance anxiety.
- Injury to the penis.
- Chronic illness such as diabetes and high blood pressure.
- Unhealthy habits like smoking, drinking too much alcohol, overeating and lack of exercise.
Low libido (reduced sexual desire)
Low libido means your desire or interest in sex has decreased. The condition is often linked with low levels of the male hormone testosterone. Testosterone maintains sex drive, sperm production, muscle, hair and bone. Low testosterone can affect your body and mood. Reduced sexual desire may also be caused by depression, anxiety or relationship difficulties. Diabetes, high blood pressure, and certain medications like antidepressants may also contribute to a low libido.
How is male sexual dysfunction diagnosed?
Your doctor may begin the diagnosis process with a physical exam. Physical tests may include:
- Blood tests to check your testosterone levels, blood sugar (for diabetes) and cholesterol.
- Blood pressure check.
- Rectal exam to check your prostate.
- Examination of your penis and testicles.
Other tests can show if you have problems with blood flow to the penis.
Your doctor may also ask questions about your symptoms and your medical and sexual history. Though these questions may seem very personal, do not be embarrassed. It is important to answer honestly so the best treatment can be recommended. You may be sent to a different type of doctor (urologist, endocrinologist or sex therapist, for example) who can help you.
How is male sexual dysfunction treated?
Many cases of sexual dysfunction can be corrected by treating the mental or physical problems that cause it. Treatments include:
- Medications: Drugs that help improve sexual function by increasing blood flow to the penis
- Hormone therapy: Low levels of testosterone raised by hormone replacement therapies that include injections, patches or gels.
- Psychological therapy: A psychological counselor to help you address feelings of anxiety, depression, fear or guilt that may affect sexual function.
Can male sexual dysfunction be prevented?
While male sexual dysfunction cannot be prevented, dealing with the causes of the dysfunction can help you better understand and cope with the problem when it happens. To help maintain good sexual function you should follow the same program that is recommended to maintain cardiovascular health.
- Follow your doctor’s treatment plan for any of your medical/health conditions.
- Limit your alcohol intake.
- Quit smoking.
- Eat a heart healthy diet (the Mediterranean diet is often recommended).
- Get regular aerobic and weight building exercise.
- Get treatment if needed for any emotional or psychological problems such as stress, depression and anxiety.
- Communicate better and more often with your partner. Sexual problems in men also affect their partners.
Sexual health is an important part of a man’s life, no matter his age, civil status, or sexual orientation. It is also an important
part of a couple’s foundation and contributes to the quality of life.
What is premature ejaculation?
Premature ejaculation is the most common of the ejaculatory disorders; approximately 20% to 30% of men will have premature ejaculation. Ejaculation problems involve the improper discharge of sperm, prostatic, and seminal vesicle fluid through the urethra.
There are three different types of premature ejaculation:
- Premature ejaculation is ejaculation after minimal or no physical stimulation.
- Retarded ejaculation is ejaculation after a long delay of physical stimulation.
- Retrograde ejaculation is orgasm without ejaculation, also called “dry” ejaculation.
What are the symptoms of premature ejaculation?
Classically, premature ejaculation includes:
- Brief ejaculatory latency
- Loss of control
- Psychological distress in the patient and/or partner
Generally, premature ejaculators will only have about a minute or less of intravaginal time before they ejaculate.
Retarded ejaculation will present as a long delay of intravaginal time to the point where the patient will not be satisfied with the sexual relation.
Anejaculation or retrograde ejaculation is the experience of a dry orgasm. The semen doesn’t go out of the urethra. It can
either flow to the bladder instead or not be produced at all. Following the sexual act in the latter case, patients will notice the presence of semen in their first urine.
What causes premature ejaculation?
There are many potential causes of premature ejaculation. These include neurological causes that affect the following areas:
- Central control of ejaculation
- Innervations to the seminal tract
- Sensory innervation to the genitalia/prostate
Premature ejaculation may be caused by negative conditioning and penile hypersensitivity. Retarded ejaculation may be an early sign of diabetes or may develop following surgery for benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). Anejaculation (retrograde ejaculation) may be caused by radical prostatectomy, cystoprostatectomy (removal of the bladder and the rectum), or the use of certain medications such as alpha-blockers (tamsulosin) and antidepressants (SSRIs)
What is the treatment for premature ejaculation?
The treatment will vary according to the cause of premature ejaculation. Couples sexual therapy or psychological therapy can be useful when psychological causes are involved. Other nonpharmacological therapies include actively trying to “hold it in.” Drug therapy has also proven to be successful. The medications used to treat premature ejaculation are selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs).
What is disordered orgasm?
Disordered orgasm is the inability to reach an orgasm after adequate stimulation.
Orgasm is still a phenomenon that is poorly understood.
What causes disordered orgasm?
The causes of disordered orgasm include:
- Psychiatric disorder
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Multiple sclerosis
- Complications from genital surgery
- Pelvic trauma
- Drugs (alpha-blockers, antidepressants)
What is the treatment for disordered orgasm?
Anorgasmia will be treated with psychiatric help or by treating the underlying cause.
What are other kinds of sexual dysfunction in men?
Another category of sexual problem is sexual pain. A penile lesion, injury, or a skin disease can be the cause among others. Men’s sexual pain occurs less frequently than women’s.
At what age do men experience sexual dysfunction?
There are normal changes in sexual function in the elderly. Older men can have the following symptoms of sexual dysfunction:
- Longer delay between stimulation and erection
- Erection is less turgid
- Ejaculation is less strong
- Ejaculatory volume is smaller
- Time between erections is longer
- Less sensitivity to tactile stimuli
- Lower testosterone
- Orgasm is attained more slowly
These phenomena can be experienced as patients grow old. Nevertheless, it can be addressed so that those affected can still have a very satisfactory sexual life.
Can sexual problems in men be prevented?
Lifestyle changes can be useful to help treat or improve sexual dysfunction, but more importantly, they can have an impact
before the development of the disease itself. You can prevent the incidence of sexual troubles by having a healthy lifestyle; exercise regularly, eat well, limit alcohol consumption, and quit smoking, if you are a smoker. Lifestyle changes take time and effort, but the results are worthwhile.
Share this page to educate others or click on the whatsapp below to talk to our Doc
